Currently Empty: $0.00
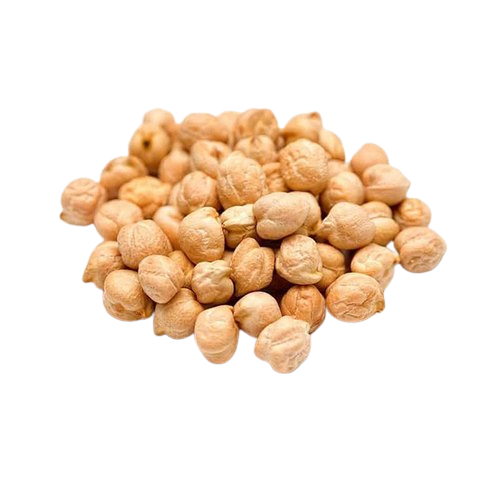
Chickpeas – Whole Kabuli
Originally cultivated in the Mediterranean and the Middle East, the chickpea (or garbanzo bean) is important in Indian and Middle Eastern cuisine. They are round and beige in colour and come with a range of potential health benefits as they are a great source of both soluble and dietary fibre. They contain several key vitamins and minerals, and are also high in protein so they are a fantastic alternative to meat for vegetarians.
Description Raw, dry, threshed, sound Kabuli Chickpeas (Cicer Arietinum)
Cream to light brown coloured in appearance, slightly round in shape with a beak like protrusion
Physical Standards
Defects – Maximum by weight %
Poor Colour 2 %
Mould 1 %
Fungal Affected e.g. Ascochyta 1 %
Total Defective 2 %
Colour Cream to light brown coloured in appearance
Flavour Chickpeas contain a nutty like flavour
Moisture Maximum 14 %
Foreign Matter Maximum by weight %
Foreign Material – includes Unmillable Material 0.5 %
Unmillable Material – Soil, Stones, Sclerotes, Non-Vegetable Matter 0.1 %
Snails Nil tolerance
Field Insects –Dead per 200g. Includes Grasshoppers and/or Locusts One (1) Max
Objectionable Material – Includes Objectional Odour, animal excreta,
wood, glass, metal** and infestation
Nil tolerance
Ryegrass Ergot Nil tolerance
** Magnets screen for metals, however not for non-ferrous and stainless steel as these metals
do not exist in the supply chain (farming equipment/production plant)
For full control, own risk assessment is advised